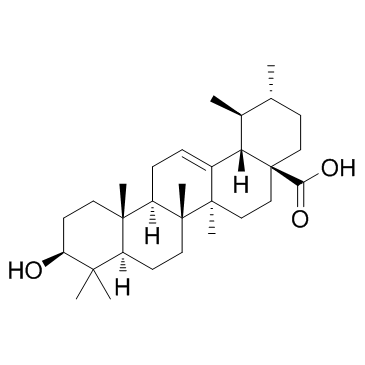
Ursolic acid
CAS No. 77-52-1
Ursolic acid( Bungeolic Acid | Maerotaine | Malol | NSC 4060 | NSC 167406 | Prunol )
Catalog No. M15928 CAS No. 77-52-1
Ursolic acid(Bungeolic acid) is a natural pentacyclic triterpenoid carboxylic acid, exerts anti-tumor effects and is an effective compound for Y prevention and therapy.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 50MG | 38 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 45 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 75 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameUrsolic acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionUrsolic acid(Bungeolic acid) is a natural pentacyclic triterpenoid carboxylic acid, exerts anti-tumor effects and is an effective compound for Y prevention and therapy.
-
DescriptionUrsolic acid(Bungeolic acid) is a natural pentacyclic triterpenoid carboxylic acid, exerts anti-tumor effects and is an effective compound for Y prevention and therapy.(In Vitro):UA induced phosphorylation of AMP-activated protein kinase alpha (AMPKα) and suppressed the protein expression of DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) in the dose-dependent manner . The combination of ursolic acid (0.5 μM) and leucine (10 μM) proved to be the most effective in promoting myogenic differentiation. The combination of ursolic acid and leucine significantly increased CK activity than treatment with either agent alone. The level of myosin heavy chain, a myogenic differentiation marker protein, was also enhanced by the combination of ursolic acid and leucine . Ursolic acid efficiently induced apoptosis, possibly via the downregulation of B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2), the upregulation of Bcl-2-associated X protein and the proteolytic activation of caspase-3. Furthermore, the activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and c-Jun N-terminal kinase was increased by the administration of ursolic acid. In addition, ursolic acid significantly suppressed the invasive phenotype of the SNU-484 cells and significantly decreased the expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 . ursolic acid (UA) potently induces the apoptosis of gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells. Further mechanistic studies revealed that the ROCK1/PTEN signaling pathway plays a critical role in UA-mediated mitochondrial translocation of cofilin-1 and apoptosis . (In Vivo):UA treatment markedly improved the survival of septic rats, and attenuated CLP-induced lung injury, including reduction of lung wet/dry weight ratio, infiltration of leukocytes and proteins, myeloperoxidase activity, and malondialdehyde content. In addition, UA significantly decreased the serum levels of tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-6, and interleukin-1β, inhibited the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 in the lung, which are involved in the productions of nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2 .
-
In VitroUrsolic acid induces phosphorylation of AMP-activated protein kinase alpha (AMPKα) and suppressed the protein expression of DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) in the dose-dependent manner. The combination of Ursolic acid (0.5 μM) and Leucine (10 μM) prove to be the most effective in promoting myogenic differentiation. The combination of Ursolic acid and Leucine significantly increase CK activity than treatment with either agent alone. The level of myosin heavy chain, a myogenic differentiation marker protein, is also enhanced by the combination of Ursolic acid and Leucine. Ursolic acid efficiently induces apoptosis, possibly via the downregulation of B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2), the upregulation of Bcl-2-associated X protein and the proteolytic activation of caspase-3. Furthermore, the activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and c-Jun N-terminal kinase is increased by the administration of ursolic acid. In addition, Ursolic acid significantly suppresses the invasive phenotype of the SNU-484 cells and significantly decreases the expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2. Ursolic acid (UA) potently induces the apoptosis of gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells. Further mechanistic studies revealed that the ROCK1/PTEN signaling pathway plays a critical role in Ursolic acid-mediated mitochondrial translocation of cofilin-1 and apoptosis.
-
In VivoUrsolic acid treatment markedly improves the survival of septic rats, and attenuated CLP-induced lung injury, including reduction of lung wet/dry weight ratio, infiltration of leukocytes and proteins, myeloperoxidase activity, and malondialdehyde content. In addition, Ursolic acid significantly decreases the serum levels of tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-6, and interleukin-1β, inhibits the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 in the lung, which are involved in the productions of nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2.
-
SynonymsBungeolic Acid | Maerotaine | Malol | NSC 4060 | NSC 167406 | Prunol
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research AreaCancer
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number77-52-1
-
Formula Weight456.7
-
Molecular FormulaC30H48O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO: 91 mg/mL (199.25 mM)
-
SMILESCC1(C)[C@@H](O)CC[C@]2(C)[C@@]3([H])CC=C4[C@]5([H])[C@@H](C)[C@H](C)CC[C@@](C(O)=O)5CC[C@](C)4[C@@](C)3CC[C@@]12[H]
-
Chemical Name3beta-Hydroxyurs-12-en-28-oic acid
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Kim M, et al. Int J Mol Med. 2015 Mar;35(3):755-62.
molnova catalog



related products
-
(+)-Puerol B 2-O-glu...
(+)-Puerol B 2''-O-glucoside is a natural product for research related to life sciences.
-
Heteroclitin G
Heteroclitin G was found as potential biomarkers of KIS blood-replenishing activity, and quantitative analysis provided a research basis for further pharmacological research.
-
Mucic Acid
Mucic acid is an aldaric acid obtained by nitric acid oxidation of galactose or galactose-containing compounds such as lactose, dulcite, quercite, and most varieties of gum.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


